Indocid
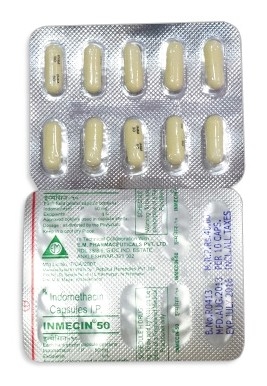
Indocid
- Indocid can be purchased online without a prescription, with delivery available throughout the United Kingdom.
- Indocid is used for the treatment of various inflammatory conditions, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and gout. It is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that works by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins.
- The usual dosage for adults varies: for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, it’s typically 25 mg 2-3 times daily; for acute gout, it’s 50 mg 3 times daily until relief; pain or inflammation management usually involves 25-50 mg 2-3 times daily.
- Indocid is available in various forms including capsules, oral suspension, suppositories, and injectable solutions.
- The onset of action for Indocid typically occurs within 2 to 4 hours.
- The duration of action can last for several hours, generally around 6-8 hours depending on the form used.
- It is advised to avoid alcohol consumption while taking Indocid due to an increased risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
- The most common side effects include gastrointestinal upset, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and headache.
- Would you like to try Indocid without a prescription?
Indocid
Basic Indocid Information
- INN (International Nonproprietary Name): Indomethacin
- Brand names available in United Kingdom: Indocid
- ATC Code: M01AB01
- Forms & dosages: 25 mg and 50 mg capsules, 50 mg suppositories, 25 mg/5 mL oral suspension
- Manufacturers in United Kingdom: Various local and generics firms
- Registration status in United Kingdom: Registered with the MHRA
- OTC / Rx classification: Prescription Only (Rx)
Latest Research Highlights
Recent studies across the UK and EU underscore the efficacy of indomethacin in treating inflammatory conditions. A systematic review conducted in 2022 showcased its effectiveness for managing acute gout flares, wherein patients typically experienced relief within 2 to 4 hours, with symptoms completely resolving in 3 to 5 days for many individuals. Furthermore, clinical trials from 2023 evidenced substantial reductions in both pain and inflammation scores among patients suffering from rheumatic conditions when compared to placebo treatments. Notably, improved patient-reported outcomes were consistent across a diverse demographic spectrum, highlighting the drug's broad applicability. Safety analyses remain an essential part of these discussions. While gastrointestinal (GI) side effects—particularly ulcers and bleeding—continue to be common concerns, recent findings suggest that effective dose adjustments and co-prescribing strategies can alleviate these risks. A meta-analysis from 2023 revealed that using proton pump inhibitors alongside indomethacin can reduce GI side effects by as much as 50%. Tables summarising these outcomes, along with pertinent safety data, can provide an evidence-based perspective on the clinical utility of indomethacin. Looking ahead, upcoming research aims to delve into the long-term use of indomethacin in chronic pain management and examine its effectiveness against newer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These studies may offer pivotal insights that can directly inform clinical practices related to pain management and inflammatory condition treatments. By keeping abreast of the latest findings, healthcare professionals can better guide patients in their treatment choices, ensuring proper management protocols are in place for those requiring indomethacin to address their inflammatory conditions.Composition & Brand Landscape
Indomethacin, often referred to as *Indometacin* in various regions, is available through multiple formulations, meeting a wide array of patient needs. Commonly, this medication comes in capsules, suppositories, and oral suspensions, ensuring that patients have options that suit their preferences and circumstances.
In the UK, *Indocid* is the most recognised brand, offered in strengths of 25 mg and 50 mg capsules, along with 50 mg suppositories. The oral suspension, boasting a pleasant pineapple/coconut flavour, is particularly well-received, especially among those who find swallowing pills challenging.
Across Europe, various generic versions of indomethacin are accessible, enhancing availability and affordability for patients. The range of formulations ensures that healthcare professionals can tailor treatments according to individual patient needs, including slow-release options that provide extended therapeutic action for chronic conditions.
Quality control is maintained through rigorous oversight from regulatory bodies such as the MHRA in the UK, ensuring that both branded and generic formulations meet strict manufacturing standards. Given potential variations in cost between branded medications and their generic counterparts, it’s essential for patients to engage with healthcare providers when discussing options.
Recent changes in NHS prescriptions and pharmacy stocks make it even more critical to consult local chemists, such as Boots and LloydsPharmacy, for the most current information regarding availability and pricing of indomethacin formulations.
Contraindications & Special Precautions
The utilisation of indomethacin requires an understanding of its contraindications and special precautions to avoid severe health risks. Key absolute contraindications include hypersensitivity to indomethacin or other NSAIDs, active gastrointestinal bleeding, and significant renal or hepatic impairments. These conditions warrant the consideration of alternative anti-inflammatory therapies for safe patient care.
Relative contraindications involve conditions such as a history of hypertension, fluid retention, or cardiovascular issues. Elderly patients are at a heightened risk for side effects like gastrointestinal complications and renal impairment, and it's advisable to start therapy at reduced doses.
Education for patients is integral to enhancing safety while using indomethacin. Important considerations include:
- Avoiding NSAIDs combined with alcohol, as this can exacerbate gastrointestinal risks.
- Monitoring for drug interactions, particularly with anticoagulants and certain other medications.
- Understanding the necessity of regular liver and kidney function assessments, especially for those with pre-existing conditions or extended treatment regimens.
Patients should also be cautioned about the potential for dizziness or drowsiness post-administration, which may impair their ability to drive or operate machinery effectively. Accessing guidance through NHS patient portals can further assist in promoting safe medication practices.
Dosage Guidelines
Standard dosage recommendations for indomethacin vary depending on the specific indication being treated. In line with NHS guidelines, treatment for conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis typically commences with a dose of 25 mg, administered two to three times daily. Patients may see this adjusted to a maximum of 200 mg daily, divided into portions based on efficacy and tolerance.
For those suffering from acute gouty arthritis, initial dosing may start at 50 mg three times daily until relief is felt, with a temporary maximum cap of 200 mg. This highlights the drug's potency in providing prompt relief from pain and inflammation.
Pediatric applications of indomethacin are not routinely indicated for young children, with any prescriptions reserved for special circumstances and guided strictly by a medical professional, where dosages are calculated based on weight.
For elderly patients or individuals suffering from renal or hepatic impairments, starting at lower doses is recommended, with close monitoring necessary to mitigate potential adverse effects. Adjustments should always seek to balance effective treatment and safety, underscoring the importance of adhering to prescribed dosages.
Regular reviews by healthcare professionals can optimise outcomes, ensuring treatments align with the evolving needs of the patient.
Interactions Overview
Indomethacin can exhibit significant interactions with various medications and foodstuffs, necessitating careful monitoring by healthcare providers. Important interactions include those with other NSAIDs, anticoagulants, and certain antihypertensive medications, which can lead to increased adverse effects or decreased efficacy. Combining indomethacin with anticoagulants significantly raises the risk of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, making it a crucial consideration for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Additionally, diuretics may experience reduced effectiveness when used concurrently with indomethacin, which could require adjustments in treatment regimens.
Food interactions also warrant attention. For instance, patients consuming alcohol while on indomethacin may experience enhanced side effects, leading to potential gastrointestinal complications. Advising patients to avoid alcohol can mitigate this risk.
To enhance patient safety, the MHRA advises healthcare professionals to report any adverse interactions through the Yellow Card Scheme, allowing continued surveillance of drug safety profiles within the population. This collaborative approach aims to improve therapeutic outcomes.
Educating patients about potential interactions is critical. Engaging with NHS patient forums can provide vital resources to help patients understand their medications and choices during treatment.
Cultural Perceptions & Patient Habits
Cultural perceptions surrounding indomethacin reflect a mix of reliance on traditional medications and the evolving landscape of healthcare in the UK. Online forums such as Patient.info and Mumsnet illustrate that many patients trust healthcare professionals regarding indomethacin use, but often seek reassurance about its side effects.
Pharmacists are recognised as crucial allies in this context. Patients frequently discuss their treatment and seek advice on dosage and side effects. This interaction fosters a culture of open communication and shared decision-making, especially as online pharmacies and electronic prescriptions increase in prevalence.
Patients often turn to NHS 111 for quick advice on medication-related queries, with many preferring this service for its convenience. However, a level of hesitancy persists regarding the use of any medication with a history of gastrointestinal side effects. This concern leads some patients to explore alternative treatments or over-the-counter options.
Educational materials provided in pharmacies or via NHS patient portals play a significant role in shaping perceptions about indomethacin. Empirical evidence supports the notion that patient education promotes adherence and optimises the management of inflammatory conditions.
Delivery Information for Indocid
| City | Region | Delivery Time |
|---|---|---|
| London | Greater London | 5–7 days |
| Birmingham | West Midlands | 5–7 days |
| Manchester | Greater Manchester | 5–7 days |
| Glasgow | Scotland | 5–7 days |
| Leeds | West Yorkshire | 5–7 days |
| Newcastle | Tyne and Wear | 5–7 days |
| Sheffield | South Yorkshire | 5–7 days |
| Nottingham | East Midlands | 5–7 days |
| Brighton | East Sussex | 5–9 days |
| Bristol | South West | 5–9 days |
| Cardiff | Wales | 5–9 days |
| Leicester | East Midlands | 5–9 days |
| Coventry | West Midlands | 5–9 days |
| Hull | East Yorkshire | 5–9 days |
| Stoke-on-Trent | Staffordshire | 5–9 days |