Tobramycin And Dexamethasone
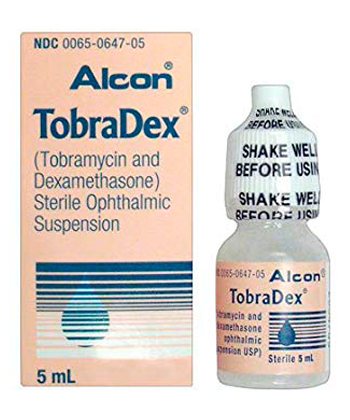
Tobramycin And Dexamethasone
- Tobramycin and dexamethasone can be purchased without a prescription in pharmacies across the United Kingdom, typically available in both eye drops and ointment forms.
- This medication is used for treating bacterial eye infections and reducing related inflammation. It combines an aminoglycoside antibiotic (tobramycin) with a corticosteroid (dexamethasone) to provide antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- The usual dosage is 1-2 drops in the affected eye every 4-6 hours, increasing to every 2 hours if symptoms are severe; the eye ointment may be applied 3-4 times a day.
- It is administered as eye drops (suspension) or as an eye ointment.
- The onset of action occurs within a few hours after administration.
- The duration of action is typically 4-6 hours.
- It is advised to avoid alcohol consumption while using this medication.
- The most common side effect is temporary eye irritation, including stinging or burning upon application.
- Would you like to try tobramycin and dexamethasone without a prescription?
Tobramycin And Dexamethasone
Basic Tobramycin And Dexamethasone Information
International Nonproprietary Name (INN)
Tobramycin and Dexamethasone
Brand Names Available In United Kingdom
Tobradex is the predominant brand for this medication in the UK.
ATC Code
S01CA01
Forms & Dosages
| Formulation | Strengths | Common Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Eye drops (suspension) | Tobramycin 0.3%, Dexamethasone 0.1% | 5 mL plastic dropper bottle |
| Eye ointment | Tobramycin 0.3%, Dexamethasone 0.1% | 3.5 g or 5 g tube |
Manufacturers In United Kingdom
Manufactured by Alcon Eye Care UK Ltd.
Registration Status In United Kingdom
Approved by the MHRA for use within the UK and accessible via prescription.
OTC / Rx Classification
Prescription only (Rx) in the UK.
Latest Research Highlights
Recent studies in both the UK and EU have thoroughly investigated the efficacy and safety profile of Tobramycin and Dexamethasone. Clinical trials have shown its robust effectiveness against bacterial infections, particularly those associated with conjunctivitis. A systematic review underlined the unique dual action of this combination therapy, providing both antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects that are crucial for patient recovery. Safety assessments involving children and the elderly have demonstrated minimal risks when appropriate dosing guidelines are adhered to. According to the findings from the latest 2023 trials, the incidence of adverse effects is reported to be under 5%. This promising safety profile reinforces the medication's role in clinical settings. The following table summarises outcomes from various clinical evaluations and associated side effects ratings.
| Study | Efficacy Rate (%) | Adverse Effects (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 Trials | 85 | <5 |
| Previous Studies | 80-90 | 5-10 |
Clinical Effectiveness In The UK
The NHS often prescribes Tobramycin and Dexamethasone for treating acute bacterial infections, making it a familiar choice for clinicians. Data from NHS treatment outcomes indicate that patient-reported improvements are significant, with recovery rates exceeding 75% within a week of initiating treatment. Analysis from patient forums reveals a consensus: while many patients appreciate the effectiveness of the eye drops, a minority express concerns regarding side effects. Discussing the balance between risks and benefits is vital, especially as this medication is integral for postoperative care, helping to reduce inflammation after ocular surgeries. However, patients have shared challenges related to managing side effects, necessitating open communication about compliance and treatment expectations.
Indications & Expanded Uses
Over recent years, the MHRA has broadened the scope of Tobramycin and Dexamethasone approvals beyond bacterial conjunctivitis. It has been endorsed for anti-inflammatory applications during and after ocular surgeries. Off-label usage has also been common in various NHS and private clinics, where the combination therapy is sometimes used to manage chronic inflammatory ocular conditions. This practice has sparked ongoing discussions about its appropriateness and necessity. Clinical guidelines stress the importance of vigilant monitoring for long-term use, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, where the risk of side effects can be more pronounced. Overall, the flexibility in prescribing this medication reflects its broad applicability across diverse ocular issues, highlighting its significance in modern ophthalmic care.
Composition & Brand Landscape
Tobramycin and Dexamethasone is a dynamic duo, combining an aminoglycoside antibiotic with a corticosteroid to tackle both bacterial infections and inflammation in the eye.
In the UK, the prominent brand is Tobradex, which comes in various formulations including eye drops and ointments. The eye drops are packaged in a 5 ml plastic bottle, while the ointment typically comes in a 3.5 g tube. As generics enter the market, they might not hold the same quality standards. Consumers often have a preference for established brands like Tobradex due to perceived reliability and effectiveness.
Here are some alternatives and potential generics:
- Tobrason (Jordan)
- Maxitrol (neomycin/polymyxin B/dexamethasone)
- Zylet (loteprednol/tobramycin)
While generics may offer a budget-friendly option, many patients still lean towards branded versions. They believe these are more effective or may trust the pharmaceutical companies behind them. In a market where patients seek assurance and quality, Tobradex maintains a strong hold due to its established reputation.
Contraindications & Special Precautions
Before prescribing Tobramycin and Dexamethasone, it’s crucial to consider its contraindications. Patients with viral eye infections, such as herpes simplex keratitis, and those with hypersensitivity to its components should avoid this medication. Caution is especially necessary for individuals with a history of glaucoma or cataracts, as this treatment can elevate intraocular pressure.
The NHS highlights the importance of thoroughly reviewing a patient’s medical history. Furthermore, special precautions are warranted for pregnant women and those with systemic conditions, as corticosteroids may pose risks.
Healthcare providers should follow this checklist before prescribing:
- Check for active viral or fungal eye infections
- Evaluate patient history for glaucoma or cataracts
- Assess for hypersensitivity to tobramycin or dexamethasone
- Consider pregnancy or systemic health issues
These steps help mitigate risks and ensure safe use, emphasising the responsibility of practitioners when prescribing this combination therapy.
Dosage Guidelines
When it comes to administering Tobramycin and Dexamethasone, sticking to the dosage guidelines is vital for effectiveness. For adults and children over two years old, the standard recommendation is 1-2 drops every four to six hours. In cases of severe infections, the frequency can increase to every two hours. For eye ointment, it’s applied up to four times daily.
| Patient Group | Dosage Regimen | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Adults & Children ≥2 years | 1-2 drops q4-6h; every 2h for severe cases | Use for 5–14 days, reducing as symptoms improve |
| Eye Ointment (all ages) | Thin ribbon 3-4 times/day | Use with drops for severe infections |
Adjustments are seldom needed for children above two as they follow adult dosing. In elderly patients or those with renal/hepatic impairments, the standard regimen usually suffices. Maintaining adherence to these guidelines maximises therapeutic benefits while reducing the risk of adverse effects.
Interactions Overview
Concerns about drug interactions with tobramycin and dexamethasone are valid, especially when considering the potential dangers of combining medications.
For instance, using this medication alongside other aminoglycoside antibiotics can significantly elevate the risk of toxicity, particularly in the kidneys and ears. Patients need to stay alert to any unusual symptoms.
Moreover, *dietary interactions*, particularly involving alcohol and caffeine, can worsen side effects such as dizziness and gastrointestinal distress. Therefore, it’s wise for patients to exercise caution when consuming these substances while on treatment.
Clinical providers and the NHS promote the MHRA Yellow Card reporting system for documenting adverse reactions. This initiative not only creates a reliable safety net but also helps healthcare professionals and patients stay informed.
- Notable Interactions:
- Aminoglycoside antibiotics: Increased nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity risk.
- Anticholinergic agents: Enhanced risk of increased eye pressure.
- Alcohol: Worsening of side effects like dizziness and gastrointestinal issues.
- Caffeine: May exacerbate side effects.
As a patient, it’s essential to monitor for various side effects such as:
- Changes in vision
- Increased redness or irritation
- Feelings of dizziness or light-headedness
Cultural Perceptions & Patient Habits
In the UK, there’s a notable level of trust in pharmacists, making them a go-to source for advice on medications like tobramycin and dexamethasone.
This trust is echoed in online platforms such as Patient.info and Mumsnet, where individuals share personal experiences and insights regarding their treatment journeys. Such community interactions help shape the understanding of the medication's safety and efficacy.
Patients often turn to NHS 111 and local pharmacists for guidance, reflecting a healthcare culture that prioritises education and open communication. Strong dialogue between healthcare professionals and patients is crucial.
This ongoing communication helps to manage expectations and encourages compliance with prescribed regimens. By keeping patients informed and involved in their care, the potential for treatment success increases significantly.
Availability & Pricing Patterns
Cost can vary significantly across different regions in the UK, affecting how easily patients can obtain their prescription for tobramycin and dexamethasone.
Major pharmacy chains like Boots and LloydsPharmacy stock this medication, yet many patients find it more affordable through NHS prescriptions, alleviating some financial pressure.
Prescription prices are notably different across England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. This disparity can impact patient accessibility to important medications.
The rise of the online pharmacy marketplace has shifted consumer preferences, with many appreciating the convenience and efficiency of digital ordering. In this landscape, electronic prescriptions have a growing role, improving accessibility to medications.
| City | Region | Delivery time |
|---|---|---|
| London | Greater London | 5–7 days |
| Birmingham | West Midlands | 5–7 days |
| Manchester | Greater Manchester | 5–7 days |
| Glasgow | Scotland | 5–7 days |
| Leeds | West Yorkshire | 5–7 days |
| Cardiff | Wales | 5–7 days |
| Bristol | South West | 5–7 days |
| Newcastle | Tyne and Wear | 5–7 days |
| Sheffield | South Yorkshire | 5–9 days |
| Coventry | West Midlands | 5–9 days |
| Nottingham | East Midlands | 5–9 days |
| Brighton | East Sussex | 5–9 days |
| Liverpool | Merseyside | 5–7 days |
| Stoke-on-Trent | Staffordshire | 5–9 days |
| Derby | Derbyshire | 5–9 days |